| Brand name | PromaCare-MAP |
| CAS No. | 113170-55-1 |
| INCI Name | Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate |
| Chemical Structure | 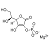 |
| Application | Whitening Cream, Lotion,Mask |
| Package | 1kg net per bag, 25kg net per drum. |
| Appearance | Free flowing white powder |
| Assay | 95% min |
| Solubility | Oil soluble Vitamin c derivative,Water soluble |
| Function | Skin whiteners |
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Storage | Keep container tightly closed and in a cool place. Keep away from heat. |
| Dosage | 0.1-3% |
Application
Ascorbic acid has several documented physiological and pharmacological effects on the skin. Among them are the inhibition of melanogenesis, the promotion of collagen synthesis and the prevention of lipid peroxidation. These effects are well known. Unfortunately, ascorbic acid has not been utilized in any cosmetic products because of its poor stability.
PromaCare-MAP, a phosphate ester of ascorbic acid, is water-soluble and stable in heat and light. It is easily hydrolyzed to ascorbic acid in the skin by enzymes (phosphatase) and it shows physiological and pharmacological activities.
Properties of PromaCare-MAP:
1) A water-soluble vitamin C derivative
2) Excellent stability in heat and light
3) Shows vitamin C activity after being decomposed by enzymes in the body
4) Approved as a whitening agent; active ingredient for quasi-drugs
Effects of PromaCare MAP:
1) Inhibitory Effects on Melanogenesis and Skin Lightening Effects
Ascorbic acid, a component of PromaCare MAP, has the following activities as an inhibitor of melanin formation. Inhibits tyrosinase activity. Inhibits melanin formation by reducing dopaquinone to dopa, which is biosynthesized in the early stage (2nd reaction) of melanin formation. Reduces eumelanin (brown-black pigment) to pheomelanin (yellow-red pigment).
2) Promotion of Collagen Synthesis
The fibers such as collagen and elastin in the dermis play important roles in the health and beauty of the skin. They hold water in the skin and provide the skin with its elasticity. It is known that the amount and quality of collagen and elastin in the dermis change and collagen and elastin crosslinks occur with aging. In addition, it is reported that UV light activates collagenase, a collagen-degrading enzyme, to accelerate the reduction of collagen in the skin. These are considered to be factors in wrinkle formation. It is well known that ascorbic acid accelerates collagen synthesis. It has been reported in some studies that magnesium ascorbyl phosphate promotes the collagen formation in the connective tissue and the basement membrane.
3) Epidermic Cell Activation
4) Anti-oxidizing Effect







